Delving into the realm of European Union laws that every online business must be well-versed in opens a gateway to understanding the intricate web of regulations governing digital commerce. From data protection to consumer rights, these laws shape the landscape in which online businesses operate, demanding compliance and strategic adaptation.
Let's explore the essential facets of EU laws that impact the online business sphere.
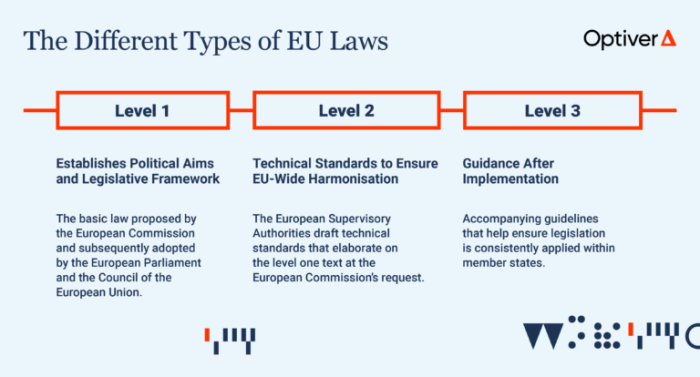
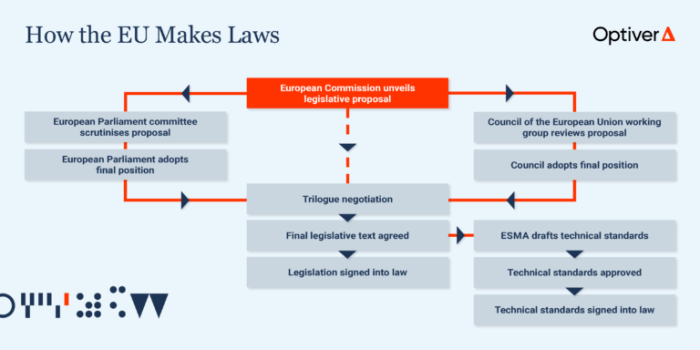
Overview of European Union Laws
Online businesses operating within the European Union are subject to a comprehensive set of laws and regulations that govern various aspects of their operations. Compliance with EU laws is crucial for online businesses to ensure legal operation, protect consumer rights, and avoid hefty fines or penalties.
Let's delve into the main categories of EU laws that impact online businesses and the key compliance requirements under these laws.
Main Categories of EU Laws Impacting Online Businesses
- Data Protection Laws: The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets strict guidelines for the collection, processing, and storage of personal data of EU citizens by online businesses.
- E-commerce Regulations: The E-commerce Directive Artikels rules related to online sales, electronic contracts, consumer rights, and obligations of online businesses.
- Cookies and Privacy Laws: The ePrivacy Directive requires online businesses to obtain consent before storing or accessing information on users' devices, such as cookies.
- Consumer Protection Laws: Regulations on unfair commercial practices, digital content, and online dispute resolution aim to safeguard consumer rights in online transactions.
Key Compliance Requirements under EU Laws
- Obtaining Consent: Online businesses must obtain explicit consent from users before collecting or processing their personal data, as per GDPR requirements.
- Transparency: Businesses must provide clear and concise information to users about data processing practices, cookie usage, and terms of service.
- Data Security: Implementing appropriate security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction.
- Right to Access and Rectification: Providing users with the ability to access their data, request corrections, and delete their information upon request.
- Compliance Monitoring: Regularly reviewing and updating data protection policies, conducting data protection impact assessments, and appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) where required.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a set of regulations aimed at protecting the personal data of individuals within the European Union. These regulations have a significant impact on online businesses that collect and process personal data.
Implications of GDPR on Online Businesses
Online businesses need to ensure that they are transparent about how they collect, use, and store personal data. They must obtain explicit consent from individuals before processing their data and have measures in place to secure this data.
- Implementing data protection policies and procedures to comply with GDPR requirements.
- Appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to oversee data protection activities.
- Conducting regular data protection impact assessments to identify and mitigate risks.
- Notifying authorities of data breaches within 72 hours of becoming aware of them.
Examples of Personal Data under GDPR Regulations
Personal data under GDPR includes any information that can be used to identify an individual, such as:
- Name and surname
- Email address
- IP address
- Location data
- Biometric data
Steps Online Businesses Need to Take to Comply with GDPR
Online businesses must take the following steps to comply with GDPR:
- Obtain explicit consent from individuals before collecting their personal data.
- Inform individuals about how their data will be used and stored.
- Ensure data is processed securely and protected from unauthorized access.
- Allow individuals to access, rectify, or delete their data upon request.
E-commerce Regulations
When it comes to e-commerce regulations in the EU, online businesses must adhere to specific laws that govern their operations. These regulations are designed to protect consumers, ensure fair competition, and uphold data privacy standards.
Comparison with Other Regions
Comparing EU e-commerce regulations with other regions can highlight differences in approach and standards. While the EU has stringent data protection laws like GDPR, other regions may have varying levels of consumer protection and privacy regulations.
Best Practices for Compliance
- Ensure transparency: Clearly display terms and conditions, pricing, and refund policies on your website.
- Obtain consent: Prior to collecting any personal data, obtain explicit consent from customers.
- Secure payment methods: Implement secure payment gateways to protect financial information.
- Data protection: Comply with GDPR requirements for handling and storing customer data securely.
- Stay informed: Keep up to date with any changes in e-commerce regulations to ensure compliance.
Consumer Protection Laws
Consumer protection laws in the European Union play a crucial role in safeguarding the rights of consumers in online transactions
Consumer Rights in Online Transactions
- Right to clear information: Consumers have the right to receive clear and transparent information about the products or services they are purchasing online, including details on pricing, terms and conditions, and delivery.
- Right to withdrawal: EU laws grant consumers a cooling-off period, allowing them to cancel a purchase within a specified timeframe without providing a reason.
- Right to redress: In case of issues with a product or service, consumers have the right to seek redress, such as refunds, replacements, or repairs.
Ensuring Compliance with Consumer Protection Laws
- Provide clear and comprehensive information: Online businesses should ensure that all product descriptions, pricing, and terms are clearly presented to consumers to avoid any misunderstandings.
- Implement a hassle-free return policy: Having a straightforward return process in place can help businesses comply with consumer protection laws regarding the right to withdrawal.
- Respond promptly to consumer complaints: Addressing consumer complaints in a timely and professional manner demonstrates a commitment to consumer rights and can prevent potential legal issues.
Impact on Online Business Practices
- Customer trust and loyalty: By complying with consumer protection laws, online businesses can build trust and loyalty with their customers, leading to repeat business and positive reviews.
- Legal compliance: Failure to adhere to consumer protection laws can result in fines, legal action, and damage to the reputation of the business.
- Competitive advantage: Businesses that prioritize consumer protection can differentiate themselves in the market and attract more customers who value ethical and transparent practices.
Intellectual Property Rights
Intellectual property rights play a crucial role in protecting the creations and innovations of online businesses in the European Union. These rights ensure that businesses have exclusive rights to their intangible assets, fostering innovation, creativity, and competitiveness in the digital market.
Types of Intellectual Property Rights in the EU
- Copyright: Protects original literary, artistic, musical, and dramatic works.
- Trademarks: Safeguard brands, logos, and slogans used to identify goods or services.
- Patents: Grants exclusive rights to inventions for a limited period.
- Design Rights: Protects the appearance of products, including shapes, colors, and patterns.
- Trade Secrets: Safeguards confidential business information that provides a competitive advantage.
Protecting Intellectual Property Rights Online
Online businesses can take several measures to safeguard their intellectual property rights in the EU:
- Registering trademarks, patents, and designs with the European Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO).
- Implementing robust copyright policies to protect digital content such as images, videos, and written materials.
- Using watermarks and digital rights management (DRM) tools to prevent unauthorized use of creative works.
- Monitoring online platforms for infringement and taking legal action against violators.
- Entering into licensing agreements to grant permission for the use of intellectual property while retaining ownership.
Cybersecurity Regulations
In today's digital world, online businesses face numerous cybersecurity threats that can compromise sensitive data and harm their operations. It is crucial for online businesses operating in the European Union to meet cybersecurity requirements to protect themselves and their customers from potential cyber attacks.
Cybersecurity Threats Faced by Online Businesses
- Phishing attacks: Cybercriminals send fraudulent emails or messages to deceive employees or customers into revealing sensitive information.
- Ransomware: Malicious software that encrypts data and demands a ransom in exchange for decryption keys, threatening to leak the data if the ransom is not paid.
- DDoS attacks: Distributed Denial of Service attacks overwhelm a website with traffic, causing it to crash and become unavailable to legitimate users.
- Data breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data, leading to its theft or exposure, resulting in financial losses and reputational damage.
Strategies to Enhance Cybersecurity
- Implement multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security beyond passwords.
- Regularly update software and systems to patch vulnerabilities and protect against known threats.
- Educate employees and customers about cybersecurity best practices to prevent social engineering attacks.
- Conduct regular cybersecurity audits and risk assessments to identify and mitigate potential weaknesses in the system.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, navigating the European Union laws that dictate online business operations requires vigilance, adaptability, and a thorough understanding of the legal landscape. By adhering to these regulations and staying informed of updates, online businesses can thrive in the ever-evolving digital ecosystem while building trust with consumers and safeguarding their operations.
FAQ Guide
What are the key compliance requirements under EU laws for online businesses?
Online businesses must ensure compliance with GDPR, e-commerce regulations, consumer protection laws, intellectual property rights, and cybersecurity regulations.
How can online businesses protect their intellectual property rights in the EU?
Online businesses can protect their intellectual property rights by registering trademarks, copyrights, and patents, and by enforcing IP protection through legal means.
What are some common cybersecurity threats faced by online businesses in the EU?
Common cybersecurity threats include data breaches, phishing attacks, malware infections, and ransomware incidents that can compromise sensitive information and disrupt business operations.







