Embarking on a journey through the intricate world of regulatory challenges for e-businesses in Europe, we uncover the complexities and nuances that shape the digital marketplace in this region. From data protection to cross-border operations, each aspect plays a crucial role in shaping the success and compliance of online businesses.
As we delve deeper into the details, a clearer picture emerges of the regulatory framework that governs e-commerce activities across various European countries.
Overview of Regulatory Challenges for E-Businesses in Europe
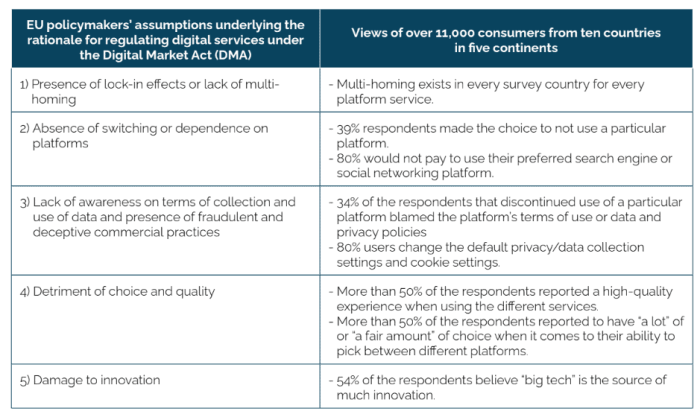
Operating an e-business in Europe comes with a set of regulatory challenges that must be navigated to ensure compliance and success in the market. The regulatory landscape in Europe is complex and constantly evolving, requiring businesses to stay updated on the latest regulations and adapt their operations accordingly.
Key Regulations Impacting E-Business Operations
There are several key regulations that significantly impact e-business operations in Europe:
- The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This regulation governs the collection and processing of personal data of individuals within the EU. E-businesses must ensure they are compliant with GDPR requirements to protect the privacy and rights of their customers.
- The e-Commerce Directive: This directive establishes rules for online service providers, including liability exemptions for certain types of content. E-businesses need to adhere to these rules to avoid legal issues.
- The Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2): This directive regulates payment services in the EU, including online payments. E-businesses must comply with PSD2 requirements to ensure secure and transparent payment processes for customers.
Importance of Regulatory Compliance in the European Market
Complying with regulatory requirements in the European market is crucial for e-businesses for several reasons:
- Legal Compliance: Non-compliance with regulations can result in fines, legal actions, and damage to the reputation of the business.
- Trust and Reputation: Adhering to regulations demonstrates a commitment to protecting customer data and rights, enhancing trust and reputation among consumers.
- Market Access: Compliance with regulations is often a requirement for accessing the European market, ensuring that e-businesses can operate legally and effectively in the region.
GDPR Compliance for E-Businesses
With the implementation of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), e-businesses operating in Europe need to ensure compliance with strict data protection rules to protect the personal information of their customers.
Implications of GDPR for E-Businesses
- E-Businesses must obtain explicit consent from individuals before collecting their personal data.
- They need to ensure that the data collected is processed securely and transparently.
- Companies must appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to oversee GDPR compliance.
Ensuring GDPR Compliance
- Implementing privacy policies and terms of service that clearly Artikel how personal data is collected and processed.
- Regularly conducting data protection impact assessments to identify and mitigate risks to data security.
- Providing customers with the option to access, correct, or delete their personal data upon request.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
- Companies that fail to comply with GDPR regulations can face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of their annual global turnover, whichever is higher.
- Non-compliance can also damage the reputation of e-businesses and lead to loss of customer trust.
Cross-border E-Commerce Regulations
Operating across different European countries presents unique challenges for e-businesses due to varying e-commerce regulations in each country.
Comparison of Key European Countries' E-Commerce Regulations
- Germany: Known for strict consumer protection laws, e-businesses must adhere to regulations on data privacy, return policies, and product labeling.
- France: E-commerce regulations in France focus on consumer rights, requiring transparent pricing, clear terms, and conditions, and secure online payment methods.
- United Kingdom: Post-Brexit, the UK has its own set of e-commerce regulations, including VAT requirements, consumer protection laws, and data protection regulations.
- Spain: E-businesses operating in Spain must comply with regulations on information disclosure, data protection, and electronic contracts.
Strategies for Navigating Cross-border Regulatory Challenges in E-Commerce
- Conduct thorough research: Understand the e-commerce regulations of each country you operate in to ensure compliance.
- Seek legal counsel: Consult with legal experts in each country to navigate complex regulations and ensure compliance.
- Implement a robust compliance program: Develop internal policies and procedures to ensure adherence to various e-commerce regulations.
- Use technology solutions: Invest in software tools that can help automate compliance processes and monitor regulatory changes across different countries.
Consumer Protection Laws and E-Businesses
Consumer protection laws play a crucial role in shaping the e-business landscape in Europe. These regulations are designed to safeguard the rights of consumers and ensure fair and transparent transactions in the digital marketplace.
Impact of Consumer Protection Laws on E-Business Practices
Consumer protection laws in Europe have a significant impact on how e-businesses operate. These laws dictate the obligations that businesses must adhere to when selling goods or services online. Some key aspects include:
- Clear and transparent pricing: E-businesses must provide accurate pricing information, including taxes and fees, to consumers before they make a purchase.
- Right of withdrawal: Consumers have the right to cancel a purchase within a specified period and receive a full refund. E-businesses must clearly communicate this right to consumers.
- Data protection: E-businesses must comply with data protection laws, such as GDPR, to ensure the security and privacy of consumers' personal information.
Common Issues E-Businesses Encounter in Relation to Consumer Protection Regulations
E-businesses often face challenges in complying with consumer protection laws due to various reasons. Some common issues include:
- Failure to provide clear and accurate information: E-businesses may run into trouble if they do not accurately disclose pricing, terms and conditions, or refund policies to consumers.
- Non-compliance with data protection regulations: E-businesses that mishandle consumer data or fail to obtain proper consent for data processing can face hefty fines and damage to their reputation.
- Deceptive marketing practices: E-businesses must refrain from misleading advertising or false claims about their products or services to avoid legal repercussions.
Best Practices for E-Businesses to Ensure Compliance with Consumer Protection Laws
To navigate the complex landscape of consumer protection regulations, e-businesses can adopt the following best practices:
- Provide clear and detailed information: E-businesses should ensure that all pricing, terms and conditions, and refund policies are clearly communicated to consumers before they make a purchase.
- Obtain explicit consent for data processing: E-businesses must obtain consent from consumers before collecting and processing their personal data, as required by data protection laws.
- Regularly review and update policies: E-businesses should stay informed about changes in consumer protection laws and update their policies and practices accordingly to remain compliant.
Payment Regulations for E-Businesses in Europe
When it comes to operating e-businesses in Europe, companies need to adhere to specific payment regulations to ensure compliance and security in online transactions.
Impact of Payment Services Directive (PSD2) on E-Commerce Businesses
The Payment Services Directive (PSD2) is a regulatory framework that aims to enhance the security of electronic payments in the European Union. It requires e-commerce businesses to implement strong customer authentication measures for online transactions, such as two-factor authentication, to reduce the risk of fraud and enhance consumer protection.
Securing Online Transactions while Complying with Payment Regulations
- Implementing strong encryption protocols to protect sensitive payment information.
- Using secure payment gateways that comply with PCI DSS standards to ensure the safe transmission of payment data.
- Regularly monitoring and updating security measures to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.
- Providing clear and transparent payment policies to customers, including information on payment methods accepted, transaction fees, and refund policies.
Last Point
In conclusion, the landscape of regulatory challenges for e-businesses in Europe is multifaceted and ever-evolving. By understanding and adhering to these regulations, businesses can not only thrive but also build trust with their customers in this dynamic digital ecosystem.
FAQ Overview
Are there specific regulations that e-businesses need to follow in Europe?
Yes, there are key regulations such as GDPR, cross-border e-commerce regulations, consumer protection laws, and payment regulations that impact e-business operations in Europe.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with GDPR in Europe?
Non-compliance with GDPR can result in hefty fines, with penalties reaching up to 4% of a company's global annual turnover or €20 million, whichever is higher.
How can e-businesses ensure GDPR compliance in their operations?
E-businesses can ensure GDPR compliance by implementing data protection measures, conducting regular audits, obtaining user consent for data processing, and appointing a Data Protection Officer.
What is the impact of the Payment Services Directive (PSD2) on e-commerce businesses?
The Payment Services Directive (PSD2) aims to make online payments more secure and promote innovation in the payment industry by allowing third-party providers access to bank accounts for initiating payments.










![Home based Business Ideas from Your Home [INFOGRAPHIC] Home based Business Ideas from Your Home [INFOGRAPHIC]](https://business.viralsumsel.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Home-based-Business-Ideas-from-Your-Home-Tycoonstory-1920x1195-1-300x178.jpg)